Advertisement
Managing different Python versions on your computer doesn’t have to be complicated. That's where pyenv steps in. If you ever felt stuck juggling projects that need different Python versions, you’re going to love how simple pyenv makes it. It lets you easily switch between versions without creating any mess on your system. Whether you’re working on an old Django project or the latest data science experiment, pyenv keeps everything clean and organized.
Most systems already come with a version of Python installed. The problem? It's often outdated. Plus, different projects require different versions. If you manually install and switch Python versions, you can quickly end up with conflicts, broken environments, and a lot of unnecessary frustration.
Pyenv fixes all that by letting you install and manage multiple versions of Python side-by-side. You get to pick the exact version you want for each project. Even better, it won’t interfere with your system’s default Python. Think of it like having a magic remote control that lets you change your Python version anytime you want — without needing to reboot your system or fix broken packages afterward.
The best part? pyenv is lightweight, easy to use once you get the hang of it, and it saves you from a lot of unnecessary headaches down the road.
It’s especially useful if you’re someone who likes working on multiple projects at once, where each one has its own specific requirements. Instead of adjusting everything manually or running into system-wide issues, pyenv keeps things clean, separated, and stress-free.
Before jumping into installation, make sure you have a few basic tools ready. You’ll need curl, git, build-essential, and other dependencies that your operating system might ask for. These help pyenv compile and install different Python versions properly.
If you're on macOS, the simplest way to install pyenv is by using Homebrew:
bash
CopyEdit
brew update
brew install pyenv
On Ubuntu or Debian-based systems, you’ll want to run:
bash
CopyEdit
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y make build-essential libssl-dev zlib1g-dev \
libbz2-dev libreadline-dev libsqlite3-dev wget curl llvm \
libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev xz-utils tk-dev libffi-dev liblzma-dev
curl https://pyenv.run | bash
After installing, you’ll need to add pyenv to your shell’s startup file. This ensures that every time you open a new terminal, pyenv is available. Depending on your shell, it could be .bashrc, .bash_profile, .zshrc, or .profile. Add the following lines:
bash
CopyEdit
export PATH="$HOME/.pyenv/bin:$PATH"
eval "$(pyenv init --path)"
eval "$(pyenv init -)"
Reload your shell by closing and reopening your terminal, or run:
bash
CopyEdit
source ~/.bashrc
(or whichever file applies).
Once done, typing pyenv should show you a list of available commands. Congratulations, you’re all set up!
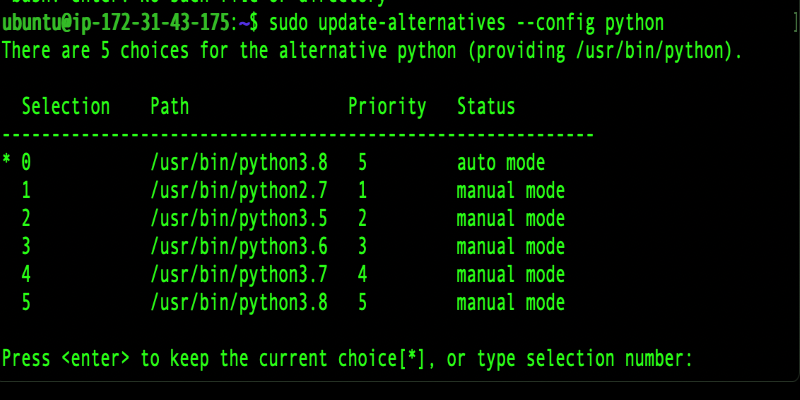
If you run into any trouble during setup, double-check that your shell configuration is correct and that you installed all the necessary dependencies. Most issues with pyenv usually come from missing packages or not updating the shell properly.
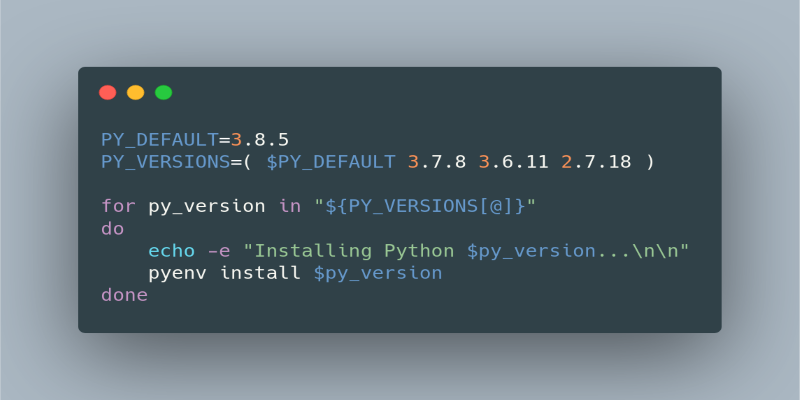
Now for the fun part. Installing a new version of Python is as easy as:
bash
CopyEdit
pyenv install 3.11.2
You can replace 3.11.2 with any version you need. To see a full list of installable versions:
bash
CopyEdit
pyenv install --list
Once your version is installed, you can set it globally (for your entire system) like this:
bash
CopyEdit
pyenv global 3.11.2
Or, if you want a specific version for just one project directory:
bash
CopyEdit
pyenv local 3.8.10
This creates a .python-version file in the project folder, telling pyenv to automatically use that version whenever you’re in that folder.
Switching between versions is automatic based on where you are in your system. If you move into a project folder that has a specified local version, Pyenv will switch to it without asking. Step outside, and it will go back to the global version. No manual commands needed, no fuss.
If you ever need to check which Python version pyenv is currently using:
bash
CopyEdit
pyenv version
Or, if you want to see all installed versions on your system:
bash
CopyEdit
pyenv versions
Everything stays neat, and you’re in full control.
One thing to keep in mind: when installing a new Python version with pyenv, it compiles from the source. So, it might take a little while, depending on your machine's speed. But it's usually a one-time thing per version, and after that, switching is instant.
Once you’re comfortable using pyenv, a few small tweaks can make your experience even smoother.
First, there’s pyenv-virtualenv. This plugin lets you create and manage virtual environments directly through pyenv. You install it like this:
bash
CopyEdit
brew install pyenv-virtualenv
or
bash
CopyEdit
git clone https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-virtualenv.git $(pyenv root)/plugins/pyenv-virtualenv
Then, add these lines to your shell startup file (right after the pyenv init lines):
bash
CopyEdit
eval "$(pyenv virtualenv-init -)"
Now, you can create a virtual environment tied to a specific Python version:
bash
CopyEdit
pyenv virtualenv 3.11.2 myenv311
And activate it with:
bash
CopyEdit
pyenv activate myenv311
Or deactivate it:
bash
CopyEdit
pyenv deactivate
Using virtual environments makes your projects even more isolated. You avoid mixing up packages across different projects, and your global Python stays clean.
Another tip: if you’re managing multiple projects, setting a local virtual environment per project keeps everything even more self-contained. It keeps project-specific dependencies from leaking into other projects, which is especially useful if you’re working with different package versions.
And one last suggestion: Always keep your pyenv updated. If you installed it with Homebrew:
bash
CopyEdit
brew update
brew upgrade pyenv
Or if you installed it manually:
bash
CopyEdit
cd $(pyenv root)
git pull
Updating ensures you get the latest features, better stability, and support for new Python releases as soon as they come out.
Using pyenv is one of those small changes that makes a big difference. It takes away the hassle of managing Python versions, keeps your projects running smoothly, and saves you from the confusion of version conflicts. Once you set it up, switching between Python versions feels effortless. If you’re serious about keeping your development setup clean and easy to manage, pyenv is the tool you’ll be glad you started using.
Advertisement
Find out the concepts of Teradata, including its architecture, key features, and real-world uses. Learn why Teradata remains a reliable choice for large-scale data management and analytics

Using ChatGPT on a Mac? Learn how to make it feel like a native part of your workflow with tips for setup, shortcuts, and everyday tasks like writing, scripting, and organizing

What makes Google Maps so intuitive in 2025? Discover how AI features like crowd predictions and eco-friendly routing are making navigation smarter and more personalized.

Not sure how Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning differ? Learn what each one does, how they work together, and why it matters when building or using AI tools.

How can Tableau enhance your data science workflow in 2025? Discover how Tableau's visual-first approach, real-time analysis, and seamless integration with coding tools benefit data scientists

AWS SageMaker suite revolutionizes data analytics and AI workflows with integrated tools for scalable ML and real-time insights

How can AI make your life easier in 2025? Explore 10 apps that simplify tasks, improve mental health, and help you stay organized with AI-powered solutions

Learn how to create professional videos with InVideo by following this easy step-by-step guide. From writing scripts to selecting footage and final edits, discover how InVideo can simplify your video production process

New to ChatGPT? Learn how to use OpenAI’s AI assistant for writing, organizing, planning, and more—no tech skills needed. Here’s how to start and get better results fast

Discover how GenAI transforms supply chain management with smarter forecasting, inventory control, logistics, and risk insights

Thinking of running an AI model on your own machine? Here are 9 pros and cons of using a local LLM, from privacy benefits to performance trade-offs and setup challenges

Looking for a quicker way to create documents in Word? Learn how to use ChatGPT to automate your document writing process directly within Microsoft Word